Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome
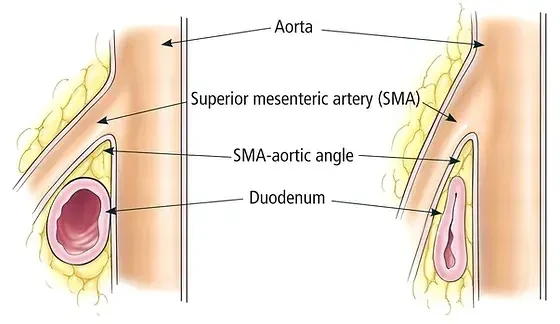
Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome (SMAS) is a rare but severe condition where the small intestine becomes compressed between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. This compression obstructs the normal flow of food through the digestive system, leading to painful and potentially dangerous symptoms. If left untreated, SMAS can result in complications like chronic malnutrition or intestinal blockages.
Symptoms of Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome (SMAS)
The symptoms of Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome (SMAS) can vary depending on the severity of the intestinal compression, but they generally affect the digestive system and can worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and fullness
- Severe weight loss
- Acid reflux or heartburn
- Constipation or bowel obstruction
Since these symptoms are non-specific and overlap with other gastrointestinal conditions, SMAS is often misdiagnosed or undiagnosed for extended periods. If you are experiencing any combination of these symptoms, particularly after rapid weight loss or abdominal surgery, it’s essential to seek a medical evaluation to rule out SMAS and begin appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of SMAS
Doppler Ultrasound
Assesses blood flow in real-time and detects compression of the small intestine. This technique is crucial for identifying any abnormal blood flow patterns caused by arterial compression in SMAS.
CT Scans
Provide detailed cross-sectional images to determine the severity of the obstruction. CT scans help visualize the exact location of the intestinal compression and any associated anatomical changes.
Upper Endoscopy
A minimally invasive procedure to visually inspect the digestive tract and evaluate the condition of the stomach and duodenum. This allows for a direct assessment of any blockages or damage caused by SMAS.
SMAS Surgical Treatment Options
Laparoscopic Duodenojejunostomy
A minimally invasive procedure that creates a bypass around the compressed intestine area, relieving the blockage and improving digestive flow.
Robotic Duodenojejunostomy
This advanced procedure uses robotic surgery for SMA syndrome, allowing for greater precision and control during the operation. Robotic techniques enhance surgical accuracy, reduce recovery time, and minimize post-operative complications.
Gastrojejunostomy
This procedure connects the stomach directly to the jejunum (another part of the small intestine) to bypass the duodenum. Using small incisions, the surgeon reroutes the digestive tract to improve food passage and alleviate symptoms caused by the obstruction.
Transabdominal Duodenojejunostomy
A traditional surgical approach where the intestine is rerouted to bypass the obstruction. This procedure reroutes the intestine to bypass the compression, offering a durable solution for severe cases of intestinal obstruction.
The Impact of SMAS on Quality of Life

Superior Mesenteric Artery SMA Syndrome can greatly impact a patient’s quality of life. The chronic pain, malnutrition, and digestive discomfort caused by this condition often affect daily activities, social interactions, and emotional well-being. Dr. Tierney and our dedicated team understand the physical and emotional challenges of SMAS and work to provide personalized care that addresses every aspect of the patient’s experience.
Through advanced diagnostics, non-invasive therapies, and expert surgical interventions, we help patients regain their health, restore their digestive function, and improve their overall quality of life.
Before surgery
Preparing for surgery involves several key steps to ensure the best outcomes. These steps include:
- Consultation and Evaluation: A detailed consultation is conducted where your medical history is reviewed, and a physical exam is performed to determine the best treatment plan.
- Diagnostic Testing: Comprehensive imaging and diagnostic tests, such as CT scans or Doppler ultrasounds, are completed to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of SMAS.
- Pre-Surgical Planning: Our team carefully plans the procedure if surgery is needed, ensuring a minimally invasive approach whenever possible.
After surgery
The type of surgical procedure you undergo will determine the post-operative care required. Generally, post-surgery care involves:
- Hospital Stay: For minimally invasive surgeries like robotic duodenojejunostomy, hospital stays are typically short. Most patients can expect to be discharged within 1-2 days, depending on their recovery progress.
- Post-Operative Monitoring: Post-surgical care focuses on monitoring your recovery, managing pain, and ensuring the resumption of normal digestive function. Our team will monitor for any potential complications and provide tailored rehabilitation plans.
- Follow-Up Care: A follow-up appointment will be scheduled within one week after surgery to check your progress and ensure you are healing properly.
